-
Appointments
Outpatient (OP) consultation
- OP department functions between 8 am and 7 pm every day, except Sunday
- You need to fix prior appointments to consult with our specialists.
- Please call 8081 800 900 & +91422 4055155 to book an appointment
- Walk-in patients will be checked by the doctors available in the emergency department.
-
Shoulder Rehab Clinics
Shoulder Rehab Clinics
- Cuff clinic
- Instability clinic
- Elbow and wrist clinic
- Other trauma
CUFF CLINIC:
- Cuff Clinic – Monday – 3.30 PM to 5.30 PM
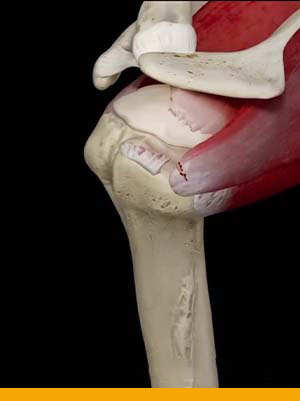
Rotator Cuff:
- The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that keep the shoulder joint stable.
These muscles also allow the shoulder to rotate safely. Rotator cuff injuries are common.
They can range from chronic inflammation to tears in one or more of the rotator cuff
tendons.
Symptoms:
- Pain when lifting and lowering your arm or with specific movements
- Popping or clicking sounds when moving your arm
- Shoulder pain that worsens at night or when resting your arm
- Shoulder weakness and struggling to lift items
- Daily activities like combing your hair or getting dressed are painful and difficult
to do.
Nonsurgical treatments:
- Arm sling and rest to give your shoulder time to heal
- Pain medications
- Activity modification
- Tailored Patient-specific Physical therapy
- Steroid injections to ease pain and swelling
Surgical treatments:
- Surgery is recommended if you have a complete tear or nonsurgical treatments don’t help a
partial tear which is done through arthroscopy ( minimally invasive surgery).
- Pre-Operative Rotator cuff tear
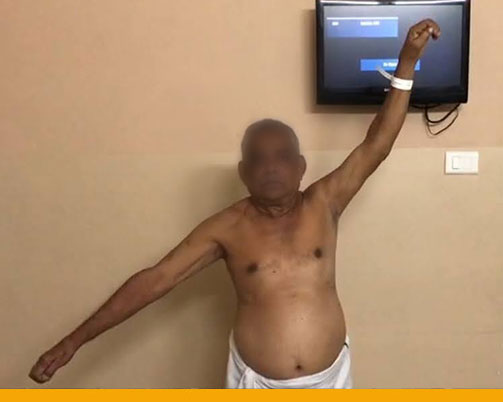
- Post Operative Improvement in Range
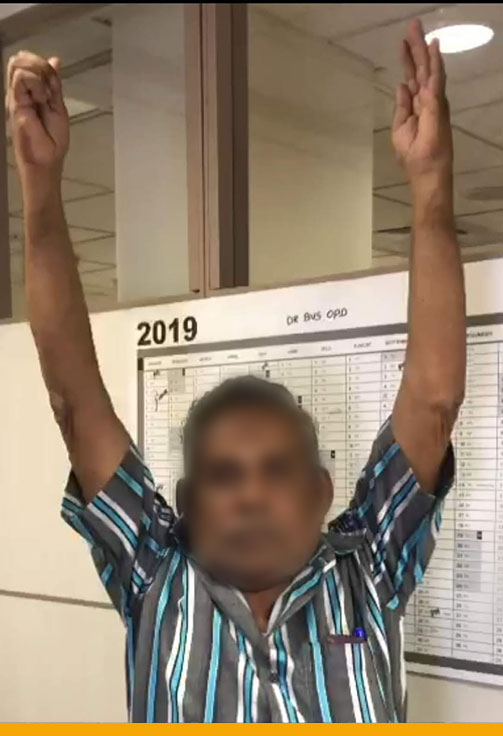

- Physical therapy:
Post-operative Immobilisation → Early Rehabilitation with Advanced Technology
- Therapeutic course of treatment offered at Ortho-One Orthopaedic SpecialtyCentre:
- Initially make the muscle to fire/work
- Electrical stimulation, Cane based exercises to improve muscle function
- Strength training will be periodically evaluated to select the amount of load
- Abnormal movements will be identified and corrected
- Technologically aided Iso-shift evaluation to make shoulder movements painless
INSTABILITY CLINIC:
Instability Clinic – Tuesday – 3.30 PM to 5.30 PM- Normal Shoulder
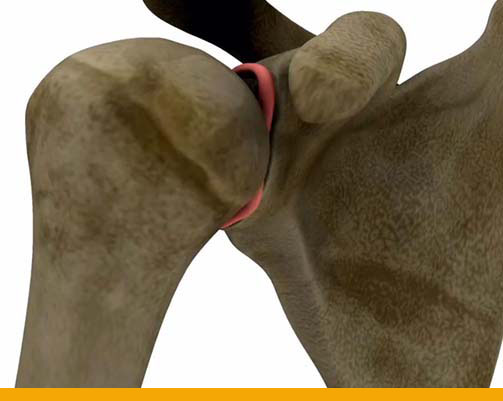
- Anterior shoulder dislocation
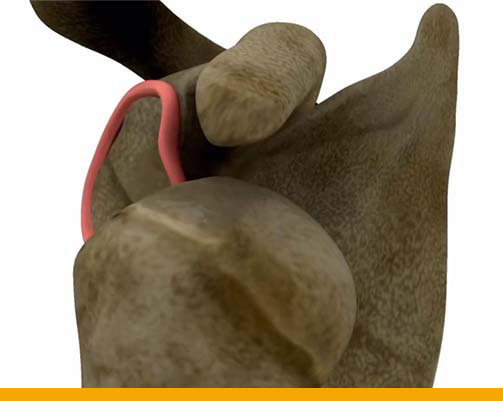

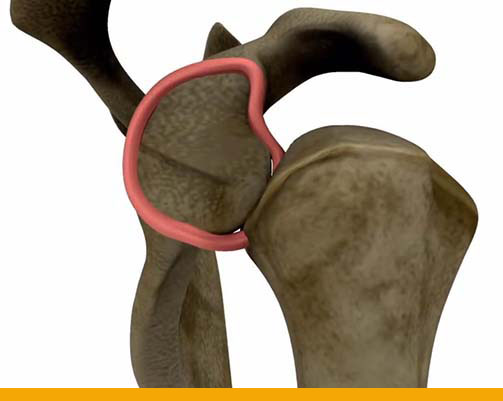
- Torn labrum (ligament)
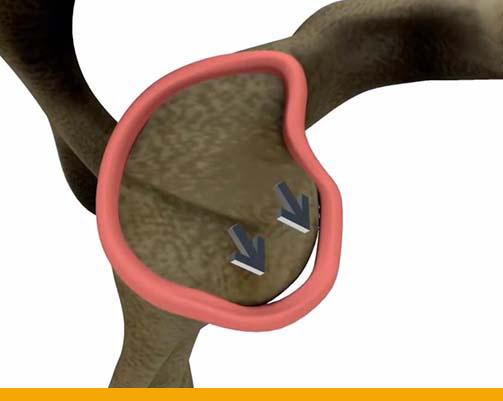
Shoulder Instability:
- When the shoulder joint is too loose and is able to slide around too much in the socket, it is
referred to as shoulder instability. In some cases, the unstable shoulder actually slips out of
the socket. If the shoulder slips completely out of the socket, it has become dislocated.
Shoulder dislocation or subluxation is usually prone to occur in the younger age group.
- Shoulder instability can happen as a result of,
- Sudden injury (can occur at any age)
- Overuse or Repetitive motions
- Shoulder laxity (loose joints)
Symptoms of Shoulder Instability:
- A feeling that the shoulder is going to come out of place with certain movements or
that the shoulder has shifted back and forth in its socket. - Clicking, catching, or looseness of the shoulder with daily activities — particularly
sports that require throwing or swimming.
Treatment for Shoulder Instability:
- Treatment depends on the severity of the instability.
Nonsurgical Treatments:
- Even nonsurgical treatment for shoulder instability usually requires a program of
supervised Rehabilitation therapy. The goal of therapy will be to strengthen the rotator cuff
and shoulder blade muscles to make the laxed shoulder more stable.
Surgical Treatments:
- If the shoulder continues to be unstable/loose after appropriate therapy, then surgery is often recommended to stabilize the shoulder.
There are a number of different procedures used to stabilize the shoulder, usually
Arthroscopic labral repair (minimally invasive procedure) or Open surgery (Laterjet
procedure).
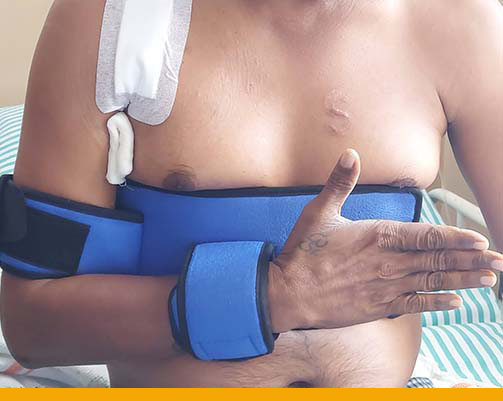
After surgery, you need to wear a Sling for about 1 month post-operatively. Then, you can
start with physical therapy to regain your range of motion and strength. Therapy is usually
necessary for 3-4 months.
Full recovery is at least 6 months to return to all sports.
- Full recovery is at least 6 months to return to all sports.
- Post – Operative Ligament repair surgery
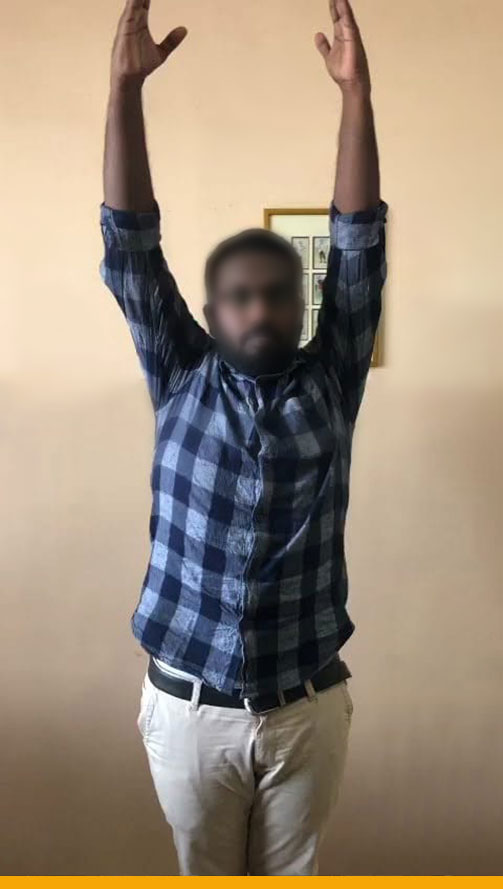
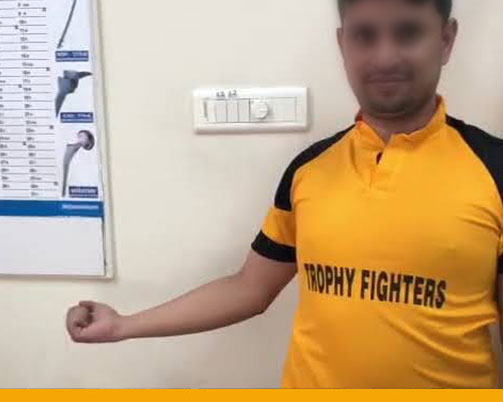


- Physical therapy: Immediate Post-operative TO Quicker Rehabilitation
- Therapeutic treatments and services offered at Ortho-one Orthopaedic Speciality Centre:
- Cryotherapy – Pain Management
- Wireless electrical stimulation – Restart muscle function
- Graded exercise program for Movements, Strength
- Posture evaluation with Technologically guided programs
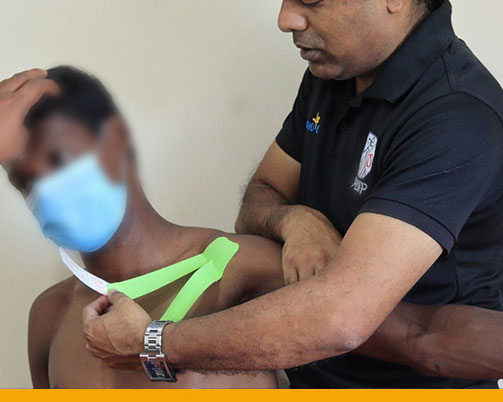
ELBOW AND WRIST CLINIC:
Elbow and wrist Clinic – Wednesday – 3.30 PM to 5.30 PM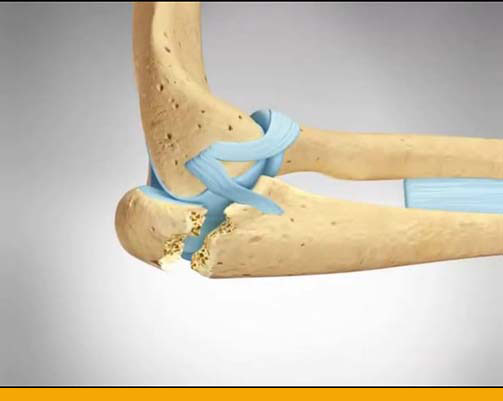
Elbow Pain:
- Overuse or repeated pressure on the tendons near the elbow joint can overload these
tissues, particularly where the tendon anchors to the bone. If overload occurs, it can cause
pain around the elbow, particularly when using the wrist and hand.
Elbow problems can vary from stiffness due to Arthritis or Trauma ( injury ) to repetitive
stress injuries like Tennis elbow or Golfer’s elbow. These overuse injuries can occur as a
result of a range of physical activities – racquet sports, rowing, canoeing, weightlifting, hockey, wrestling, swimming – as well as repetitive work tasks undertaken in a variety of
occupations. These can cause severe compromise in daily activities.
Early recognition by attending the concerned specialist can help in early diagnosis and
treatment.
Symptoms:
- Dull ache when at rest
- Pain when making a fist (golfer’s elbow)
- Pain when opening the fingers (tennis elbow)
- Soreness around the affected elbow bump
- Weak grip
- Difficulty and pain when trying to grasp objects, especially with the arm stretched
out.
Wrist pain:
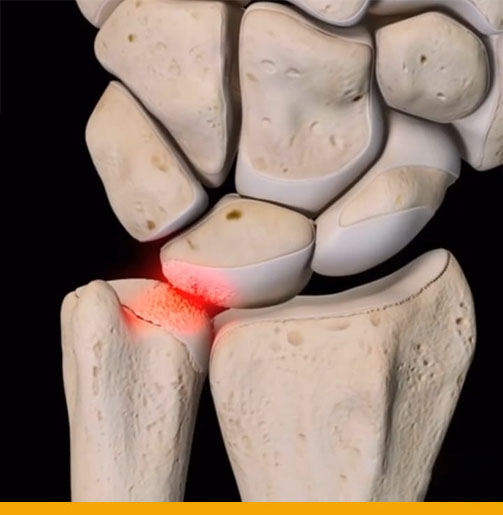
- Your wrist is a joint that connects your hand and forearm. Your wrist joint contains many
small bones that help you bend, straighten and rotate your hand and wrist. Many treatable
problems can cause pain, numbness or tingling in the wrists and hands. - Wrist Pain can be caused by a variety of factors, including simple weariness or stiffness
due to injury or a TFCC tear (wrist ligament injury) or numbness due to nerve
compression (Carpal tunnel syndrome). Wrist pain can also result from long-term
repetitive stress or arthritis.
Symptoms:
- Stiffness
- Trouble gripping objects
- A clicking sound when moving the wrist
- Based on the varying causes, some people may have pain that is achy or dull, while
others may have sharp pain. - In case of a Wrist injury – swelling and bruising
- Numbness, tingling, and hand weakness may occur when pain is due to carpal
tunnel syndrome.
Non-Surgical Treatments for Elbow and Wrist Pain:
- Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (R.I.C.E.)
- Medications
- Dry Needling
- Immobilization
- Massage
- Physical Therapy and Lifestyle modifications
- Steroid Injections
- Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
Surgical treatments for Elbow and Wrist Pain:
- Rare conditions which fail to improve with physiotherapy may warrant surgery in the form
of - Key hole surgery for ligament repair
- Open surgery / Key hole surgery for nerve release
- Key hole surgery for fracture fixation
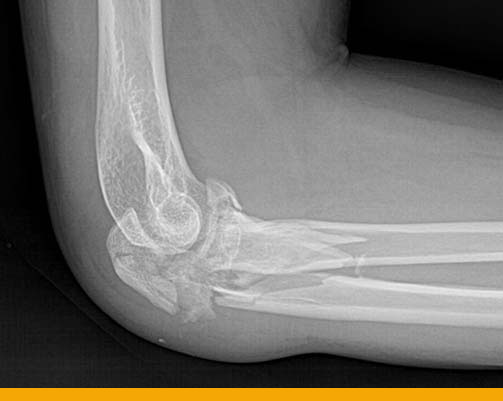
- Elbow Pre Operative X-ray
- Elbow immediate Post operative X-ray
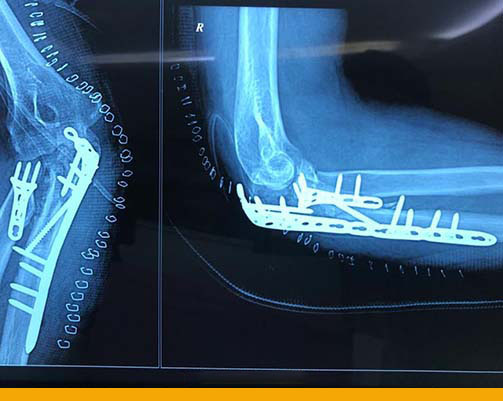
- Post Operative Elbow Replacement Surgery
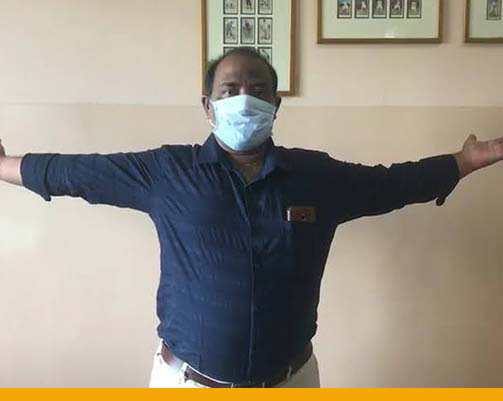
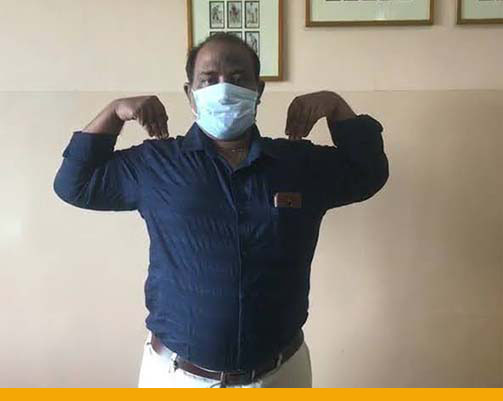


Post Operative Wrist TFCC repair surgery

Physical Therapy:
- Therapeutic course of treatment offered at Ortho-One Orthopaedic Speciality centre,
- Overcoming pain and sensitivity in the wrist and elbows
- Swelling management
- Coordinated exercise plan for wrist and fingers to improve function
- Restoration of upper limb kinetic chain
- Tailored Patient specific Physical therapy
TRAUMA CLINIC:
Other Trauma – Thursday – 3.30 PM to 5.30 PMShoulder anatomy:
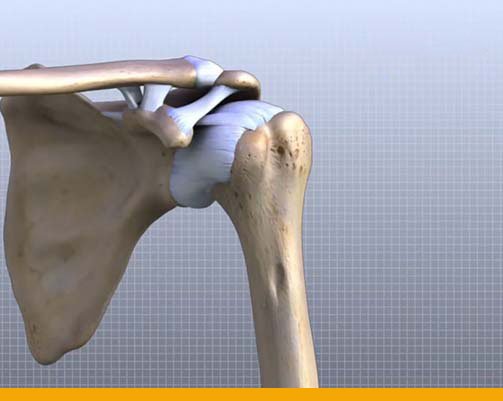
- The shoulder is made up of three bones:
- Scapula (shoulder blade)
- Clavicle (collar bone)
- Humerus (arm bone)
- These bones are joined together by soft tissues (ligaments, tendons, muscles, and joint
capsule) to form a platform for the arm to work. - The shoulder is made up of three joints:
- Glenohumeral joint
- Acromioclavicular joint
- Sternoclavicular joint
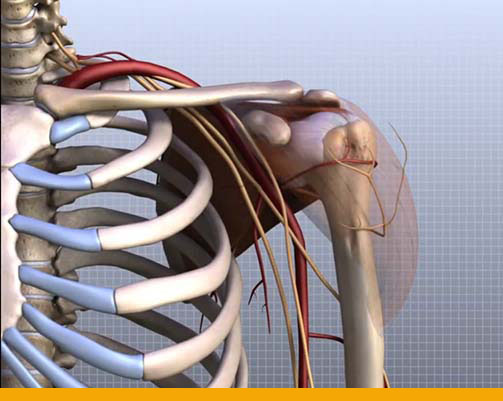
- Several layers of soft tissues cover the bones of the shoulder. The top layer, located just
beneath the skin, is the deltoid muscle. This muscle helps to bring the arm overhead, and it
gives the shoulder its rounded appearance. Beneath the deltoid muscle is the subdeltoid
bursa, a fluid-filled sac similar to a water balloon.
Shoulder Trauma:
- Trauma to the shoulder is incredibly common. Shoulder injuries most commonly occur in
athletes participating in sports such as swimming, tennis, pitching, and weightlifting. The
injuries are caused due to the over usage or repetitive motion of the arms.Trauma involving any part of the body can lead to fracture. Common treatment strategy for
fractures is to align the bone in normal continuity. If that is achievable through natural
means, Conservative treatment in the form of a POP slab or CAST application will help
ensure bone healing in 4 to 6 weeks, followed by effective rehabilitation.Displaced and angulated fractures may warrant Surgical intervention. Most importantly
fractures involving the joints are prone to non-union (failure to unite). Hence it needs
surgical intervention as early as possible.
- Reverse shoulder replacement X ray
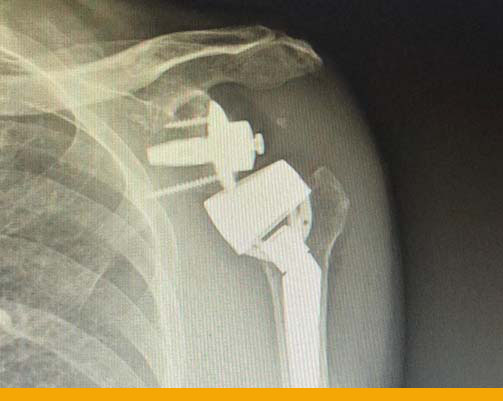
- Post surgery – Range Left Shoulder
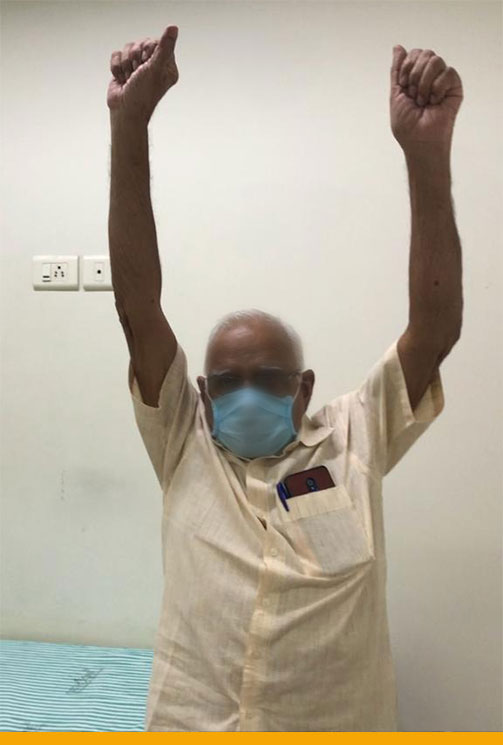
- Physical Therapy:

- Physio-Rehab services provided at Ortho-One Orthopaedic Speciality centre,
- Pain management
- Swelling management
- Scar management
- Movement restoration and strength training
Exclusive Program Highlights:
- Individualized Exercise Programs
- Physiotherapy @ Home services
- Dedicated number to contact the Physiotherapy team
- Advanced technology to help evaluate and monitor the progress of the rehabilitation
-
Knee Rehab Clinics
Knee Rehab Clinics
- Patella clinic
- Ligament clinic
- Meniscus clinic
- Osteotomy clinic
Patella Clinic
- Patella Clinic – Tuesday – 10.00 AM to 11.30 AM
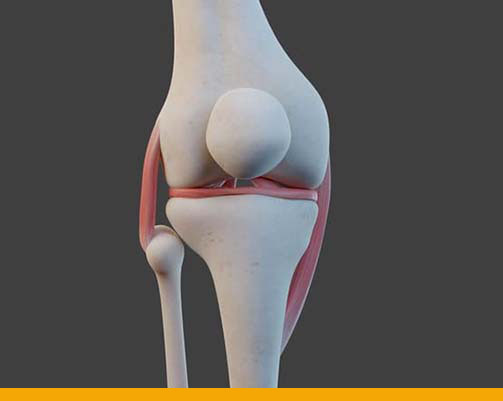
Patella:- Patella or the kneecap sits in front of the knee joint and protects the joint from damage. The
patella helps in the smooth movement of the knee in flexion and extension, and also protects
the frontal surface of the knee joint.
Patellar Instability:
- The patella (kneecap) attaches to the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone) by tendons. Thepatella fits into a groove at the end of the femur (trochlear groove) and slides up and down as
the knee bends and straightens. Patellar instability occurs when the kneecap slips out of the
femoral groove in the thigh bone.
When the patella dislocates from the trochlear groove, it can no longer move up and down.
This locks the knee and pulls the ligaments out of place, often tearing them. Patellar
dislocation is an acute injury caused by impact or by a sudden twist and turn. Like any
dislocation, it is painful and debilitating until it is corrected. But the dislocated knee cap will
sometimes correct itself.
Patellar Instability is diagnosed by taking your medical history and performing a physical
exam. X-rays / MRI / CT scan and other clinical evaluations are done with custom-made
protocols of Ortho-one.
Non-surgical treatments:
- Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (R.I.C.E.)
- Pain medications
- Activity modification
- Bracing or taping to stabilise the kneecap
- Immobilisation for 6 weeks
- Tailored Patient specific Physical Therapy
- The majority of patella dislocations spontaneously pop back into place.
Surgical treatments:
- Surgery is considered a last resort after conservative treatment has failed to relieve
symptoms.
Surgical solutions provided at Ortho-one Orthopaedic Speciality centre may be stitching the
repair, or replacing the torn ligament along with additional corrective procedures which may
correct the underlying basic cause for the injury
- MPFL Repair – Kneecap laxity repair
- MPFL Reconstruction – Kneecap ligament reconstruction
- Lateral Retinaculum Lengthening / Release – Kneecap Ligament release
- Suture Bridge fixation – Knee ligament avulsion – fixation (no implant technique)
- Kneecap mal-alignment surgeries
- Tibial Tuberosity Transfer
- Derotation Osteotomy
- Trochleoplasty
Physical therapy:
- Effective post-operative rehabilitation is as important as surgery in restoring mobility and
early return to normal daily life.
Physical therapy to benefit motion and strength is often required to maximize recovery and improve outcomes. Our Doctors and therapists will work together and advise you on when to progress with your activities and exercises.
- Patella Taping to improve patella stability
- Electrical muscle stimulation to improve muscle activity
LIGAMENT CLINIC:
- Ligament Clinic – Monday – 3.30 PM to 5.00 PM
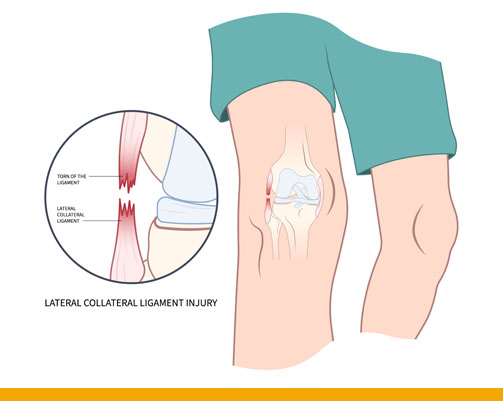
Ligament tear:
- A ligament is a band of connective tissue that attaches two bones together. Ligaments hold
them firmly in place and help you move properly. When ligaments are damaged, the knee joint may become unstable. Ligament damage often happens from a sports injury.
A ligament can be stretched or torn when it is forced to move in the wrong direction or stretches too far. This injury is called a sprain. Sprains often happen during a sudden fall, twist or impact. A torn ligament severely limits knee movement.
The knee has 4 major ligaments. They give the knee joint stability and strength. The 4 knee
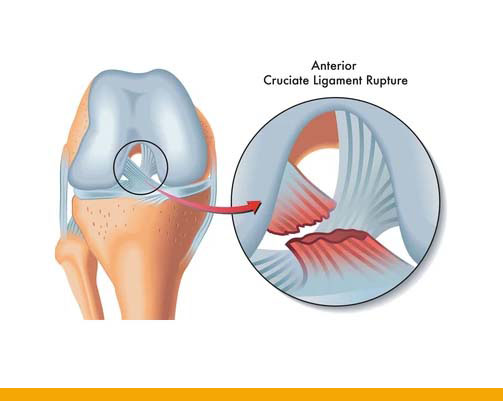
ligaments that connect the thigh bone to the lower leg’s larger bone – the shin bone) are: - Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL): This ligament is in the centre of the knee. It
controls rotation and forward movement of the shin bone.
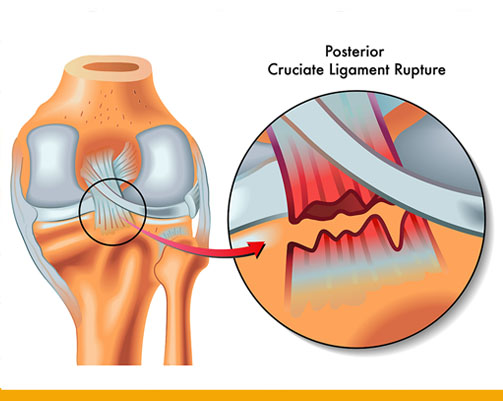
The ACL is often stretched and/or torn during sports that involve sudden stops and changes in direction – Skiing, basketball, tennis, and volleyball are sports that have a higher risk of ACL injuries. - Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL): This ligament is in the back of the knee. It
controls the backward movement of the shin bone.
The PCL injury usually occurs with sudden, direct impact, such as in a car accident or
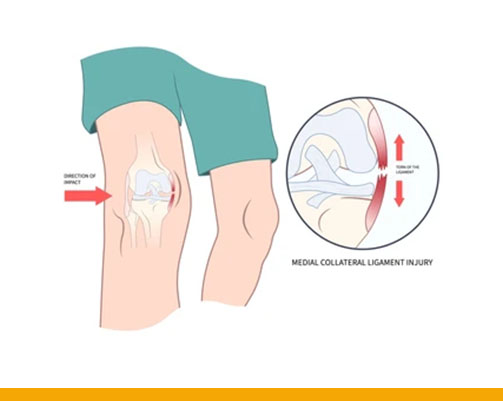
during a football tackle. - Medial collateral ligament (MCL): This ligament connects the thigh bone to the shin bone on the inside of the knee. It gives stability to the inner knee.
The MCL can tear if an injury stretches it too much. The tear might be partial or complete. Mostly occurs due to sudden changes in direction or twisting the knee while running. The MCL also can tear if the knee is hit forcefully from the side. - Lateral collateral ligament (LCL): This ligament connects the thigh bone to the
fibula, the smaller bone of the lower leg on the outer side of the knee. It gives stability to the outer knee.
LCL tears often occur in sports that require a lot of quick stops and turns such as soccer, basketball, and skiing, or ones where there are violent collisions, such as football and hockey.
Nonsurgical treatments:
- The non-surgical treatments include,
- Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (R.I.C.E.)
- Pain medications
- Protective knee brace
- Activity modification
- Using crutches during recovery
- Tailored Patient specific Physical Therapy
Surgical treatments:
- Surgery is recommended if you have a complete tear or nonsurgical treatments don’t help a
partial tear.
Surgical ligament repair treatments offered at Ortho-One Orthopaedic Speciality centre may
be stitching the repair, or replacing the torn ligament along with additional corrective
procedures which may correct the underlying basic cause for the injury - Knee ligament reconstructions
- ACL Reconstruction
- ACL Repair
- ACL Avulsion – Fixation
- ALL Reconstruction – Knee ligament reconstruction combined with Augmentation procedure
- Multi-ligament Reconstruction
- Sports-specific surgery and Rehabilitation
- Cost-effective and Biomechanically strong techniques
Physical therapy:
- Effective post-operative rehabilitation is as important as surgery in restoring mobility and
early return to normal daily life.
Physical therapy to benefit motion and strength is often required to maximize recovery and improve outcomes. Our Doctors and therapists will work together and advise you on when to progress with your activities and exercises.
- Early mobilisation post ligament surgery
- Strength testing for safe return to sports after surgery
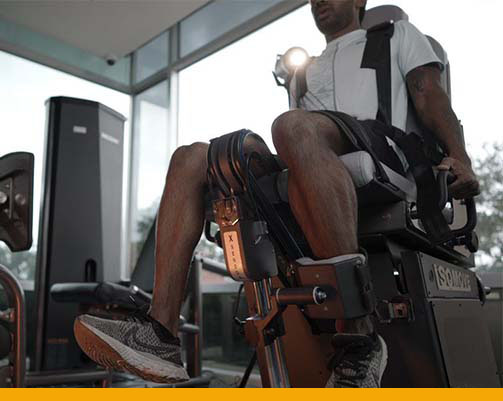

- Corrective exercises using Real Time Biofeedback

Meniscus Clinic:
- Meniscus Clinic – Thursday – 10.00 AM to 11.30 AM
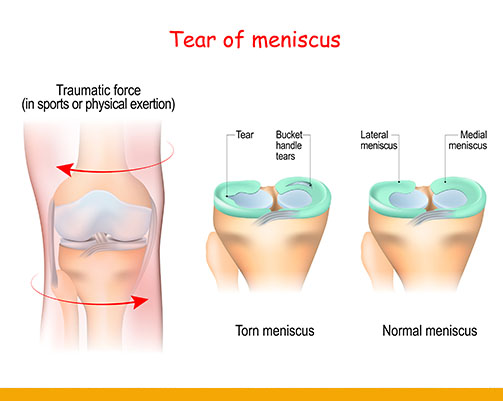
Meniscus:- Two wedge-shaped pieces of cartilage sit inside your knee, between your thigh bone (femur)
and the lower leg’s shin bone (tibia). This cartilage is called the Meniscus.
Meniscus provides cushioning for your bones and knee joint and helps transmit weight from one bone to another and keeps the knee stable. Though considered as the useless part of the knee joint, they are the shock absorbers for your knee, forming the vital part of the knee joint.
Meniscus tear:
- Meniscal tears occur when too much force is applied to a ‘normal’ meniscus or a normal
force is applied to a deteriorating meniscus.
They are commonly seen among Athletes and Elderly people. As you get older, your cartilage starts to thin, weaken, and can tear more easily. Arthritis (breakdown of cartilage in the joints) can also lead to a meniscus tear. People with deteriorated cartilage (due to age or arthritis) can tear a meniscus from simple motions like stepping on an uneven surface.
Sudden traumatic meniscus tears often occur during sports. Athletes’ whose sports activities involve sudden twisting movements like in tennis, soccer, basketball, or football, are most likely to tear a meniscus. Playing contact sports also increases the risk of a meniscal tear.
Non-surgical Treatments:
- Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (R.I.C.E.)
- Pain relief medications
- Steroid injections
- Knee brace or splints to stabilize the knee
- Tailored Patient specific Physical therapy
Surgical Treatments:
- Previously, for Meniscal tears, Cutting and removing the torn meniscus was the traditional
treatment. But now, we can repair and save the meniscus as we know it is the structure that
protects the cartilage and prevents Arthritis.
Surgical solutions provided at Ortho-one Orthopaedic Speciality centre may be stitching the repair, or replacing the torn meniscus along with additional corrective procedures which may correct the underlying basic cause for the injury - Advanced Repair Technologies
- Inside out Suture Repair
- Outside in
- All insides
- Root repair
Physical Therapy:
- Effective post-operative rehabilitation is as important as surgery in restoring mobility and
early return to normal daily life.
Physical therapy to benefit motion and strength is often required to maximize recovery and
improve outcomes. Our Doctors and therapists will work together and advise you on when to progress with your activities and exercises.
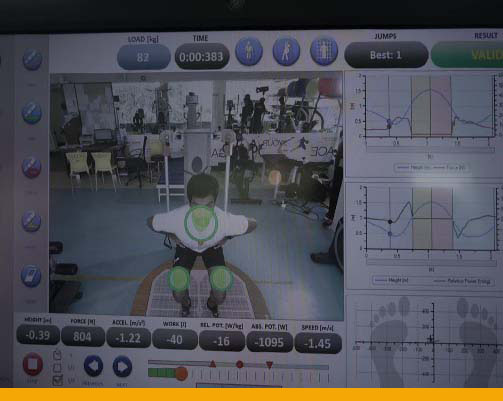
- Exercises to improve strength and stability
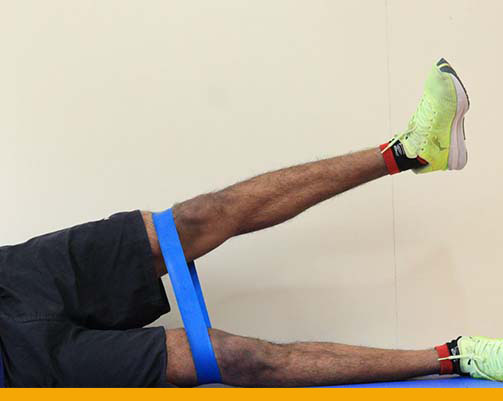

- Jump Performance assessment

Joint Preservation Clinic:
- Joint Preservation Clinic – Wednesday – 3.30 PM to 5.00 PM
Joint Preservation:
- Joint preservation is the use of non-surgical or surgical treatments to preserve a degenerating joint to delay or avoid joint replacement surgery.
The aim of joint preservation is to restore knee joint functionality while retaining the natural
structure of the affected joints. Joint preservation can be achieved through osteotomy (cutting
of the bone) to allow the realignment of the joint.
In a knee osteotomy, either the tibia (shinbone – lower leg’s larger bone ) or femur (thighbone) is cut and then reshaped to relieve pressure on one compartment of the knee joint.
Knee osteotomy is a surgical procedure used to treat the pain and dislocation that can occur
when there is damage or arthritis in part of the knee joint. For proper weight bearing, the leg
joints are aligned so that weight is distributed evenly on the knee, hence relieving pain and
significantly improving function in the affected knee. - Common Knee problems addressed in the Joint Preservation clinic (Osteotomy Clinic)
- Early Arthritis
- Mal-alignment
- Focal cartilage defects (damage to a specific area of the cartilage)
- OCD – Osteochondral defect (part of the bone and cartilage getting separated from the knee joint)
Non-surgical treatments:
- Pain medications and Cartilage protecting drugs
- Pain Modalities like IFT, Ultrasound
- Lifestyle modification and weight reduction
- Knee braces
- Steroid injections
- Tailored Patient specific Physical therapy
Surgical treatments:
- Knee Joint preservation can be achieved using minimally invasive surgery techniques in combination with the conservative approaches or if the conservative approaches fail.
Surgical treatments offered at Ortho-One Orthopaedic Speciality centre, - Osteotomy – Limb alignment correction around the Joints
- High Tibial Osteotomy – Knee joint realignment surgery
- Distal Femoral Osteotomy – Distal femur is cut, bones are repositioned and secured in proper alignment
- Tibial condylar valgus osteotomy – Limb alignment correction
- Osteochondral Transfer – Articular cartilage restoration procedure
- Orthobiologics – Use of substances naturally found in our body to help heal musculoskeletal injuries more rapidly
Physical therapy:
- Effective post-operative rehabilitation is as important as surgery in restoring mobility and
early return to normal daily life.
Physical therapy to benefit motion and strength is often required to maximize recovery and improve outcomes. Our Doctors and therapists will work together and advise you on when to progress with your activities and exercises. - Balance Testing and Training
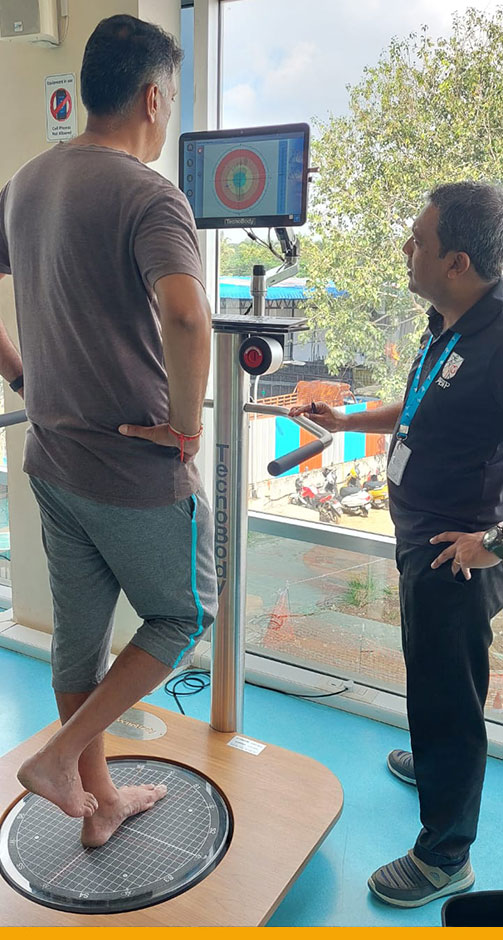

Exclusive Program Highlights:
- Individualized Exercise Programs
- Physiotherapy @ Home services
- Dedicated number to contact the Physiotherapy team
- Advanced technology to help evaluate and monitor the progress of the rehabilitation
Ask our Specialist
For specific orthopedic ailment related queries please fill in the form and get in touch with our specialistsDr. David V Rajan - Arthroscopy Surgery
Travelling Tips for Patients with Knee Pain
What is Frozen Shoulder?
Dr. P Yuvarajan-Joint Reconstruction, Hip Pre
Tips for Staying Healthy while working from Home
Rotator Cuff Tear: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Patient Success Stories
Went in for my Son's shoulder surgery last Saturday, the modern decor, pastel colors reminded me of anything but a hospi...
Read more Google reviewMarvelous service and treatment. Especially Dr.Shyamsundar and Dr.Sri Ram their great service. Keep going, thank you.
Read more Facebook reviewOne of the most caring hospital which I have encountered after a long time. From the doctors to support staff, all we t...
Read more Google reviewGreat thanks to Dr David Rajan and Dr Santhosh and team for their best effort in making my mother surgery a success owin...
Read more MeenakhiYou will not find a better Ortho hospital with so much care especially during Covid pandemic times. We had stayed for tr...
Read more Prabhu NarayanMrs. Maragatham (Name changed), a 50-year-old woman came to Ortho-One with severe pain in her right knee which affected ...
Read more Mrs. MaragathamI’m Krishnamoorthy aged 82. I had pain in both knees. Compared to all the other hospitals, I feel Ortho-One is the bes...
Read more Krishnamoorthy